IN THE NEWS

To gain further knowledge on the preclinical phase of Alzheimer’s disease (AD), we sought to characterize cognitive performance, neuroimaging and plasma-based AD biomarkers in a cohort of non-demented adults with down syndrome (DS). The goal of the down syndrome biomarker Initiative (DSBI) pilot is to test feasibility of this approach for future multicenter studies. We enrolled 12 non-demented participants with DS between the ages of 30–60 years old. Participants underwent extensive cognitive testing, volumetric MRI, amyloid positron emission...
PHYSICS
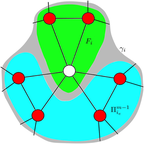
The spreading of behavior, such as the adoption of a new innovation, is influenced by the structure of social networks that interconnect the population. In the experiments of Centola, adoption of new behavior was shown to spread further and faster across clustered-lattice networks than across corresponding random networks. This implies that the “complex contagion” effects of social reinforcement are important in such diffusion, in contrast to “simple” contagion models of disease-spread which predict that epidemics would grow more efficiently on random networks than on clustered networks. To accurately model...
PSYCHOLOGY

Performing music in public is widely recognized as a potentially stress-inducing activity. However, despite the interest in music performance as an acute psychosocial stressor, there has been relatively little research on the effects of public performance on the endocrine system. This study examined the impact of singing in a low-stress performance situation and a high-stress live concert on levels of glucocorticoids (cortisol and cortisone) in 15 professional singers. The results showed a significant decrease in both cortisol and cortisone across the low-stress condition, suggesting that singing in itself...
EBOOK

Learning to read, and to spell are two of the most important cultural skills that must be acquired by children, and for that matter, anyone learning a second language. We are not born with an innate ability to read. A reading system of mental representations that enables us to read must be formed in the brain. Learning to read in alphabetic orthographies is the acquisition of such a system, which links mental representations of visual symbols (letters) in print words, with pre-existing phonological (sound) and semantic (comprehension) cognitive systems for language. Although spelling draws on the same representational knowledge base and is usually correlated with reading...