Introduction: Wires form the building block for biomedical implants in numerous disciplines, such as orthopaedic K-wires, cardiovascular stents and sutures in wound closure. Magnesium alloys were considered for wire based application more than a century ago, but failed due to high levels of impurity elements and lack of ductility[1]. In recent years Mg alloys have received significant interest as biodegradable metals. A hurdle for the widespread use of Mg alloy as biomaterials is poor corrosion resistance.
A potential breakthrough in this area came from the development of Ultra-High Purity (XHP) Mg, developed with minimal impurity levels which showed a significant increase in corrosion resistance[2]. To improve the mechanical properties of this material, several alloys were developed. XHPMg-0.45Zn-0.45Ca combines fine grain size, and minimal alloying elements to improve the strength and ductility of the XHP Mg significantly, while retaining excellent corrosion resistance and biocompatibility[3].
However, the corrosion resistance of these alloys relies on the low levels of impurity elements such as iron. These elements can be introduced to the surface of the alloy during wire production. This study aims to determine the surface treatment, which maximize the corrosion resistance of XHP Mg alloy wires.
Materials and Methods: XHPMg-0.45Zn-0.45Ca was extruded into 3 mm samples, and cold drawn into wire. This alloy is related to the alloy tested in the aforementioned study[3]. It is based from XHP Mg, alloyed with wt.% 0.45 Zn and 0.45 Ca.
The samples were tested in as drawn and as annealed conditions, as well as with a series of surface treatments including: acid cleaning, chemical polishing and mechanical grinding.
The immersion tests were conducted in bicarbonate buffered Hanks’ solution at physiological temperature and pH[4],[5].
Results: Preliminary observations and prior art suggest that appropriate surface treatment can improve the corrosion resistance of the XHP Mg alloy wire. Figure 1 demonstrates the significant impact surface treatment has had on corrosion resistance in previous studies[6].
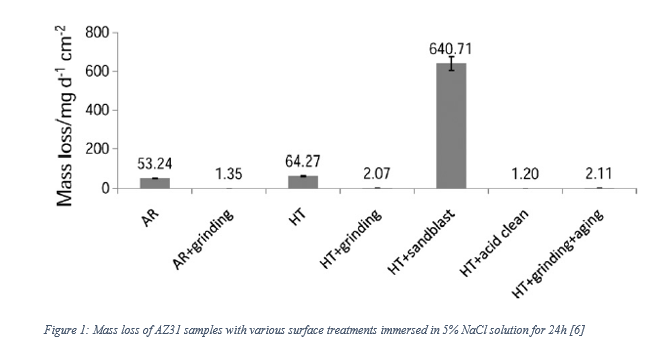
Discussion and Conclusions: If the corrosion resistance of the XHP Mg alloy wire does is found to be reduced during the wire drawing processes, the selection of an appropriate surface treatment will be an integral component in the further development of these novel materials. If none of the surface treatments prove to be effective, a novel treatment or wire production methodology will need to be considered. However, if one of the chemical surface treatments such as chemical polishing or acid cleaning is shown to be effective, this will be of particular significance as these treatments will be much more transferable to industrial processes. This will ease the future production of products manufactured from XHP Mg alloy wires.
References:
[1] F. Witte, The history of biodegradable magnesium implants: a review, Acta Biomaterialia, 6 (2010) 1680-1692.
[2] J. Hofstetter, E. Martinelli, A.M. Weinberg, M. Becker, B. Mingler, P.J. Uggowitzer, J.F. Löffler, Assessing the degradation performance of ultrahigh-purity magnesium in vitro and in vivo, Corrosion Science, 91 (2015) 29-36.
[3] J. Hofstetter, M. Becker, E. Martinelli, A.M. Weinberg, B. Mingler, H. Kilian, S. Pogatscher, P.J. Uggowitzer, J.F. Löffler, High-strength low-alloy (HSLA) Mg–Zn–Ca alloys with excellent biodegradation performance, JOM, 66 (2014) 566-572.
[4] S. Johnston, Z. Shi, A. Atrens, The influence of pH on the corrosion rate of high-purity Mg, AZ91 and ZE41 in bicarbonate buffered Hanks' solution, Corrosion Science, Accepted for publication, 20 Sept, 2015
[5] NI Zainal Abidin, B Rolfe, H Owen, J Malisano, D Martin, J Hofstetter, PJ Uggowitzer, A Atrens, The in vivo and in vitro corrosion of high-purity magnesium and magnesium alloys WZ21 and AZ91, Corrosion Science 75 (2013) 354-366
[6] G.-L. Song, Z. Xu, The surface, microstructure and corrosion of magnesium alloy AZ31 sheet, Electrochimica Acta, 55 (2010) 4148-4161.